Granulomatous Rosacea Treatment Plan Summary
Biopsy Result:
Granulomatous dermatitis with perifollicular collections of histiocytes surrounded by lymphocytes and plasma cells.
Laboratory Studies:
Baseline lab — Triglycerides: 132 (Normal <150 mg/dL)
Diagnosis:
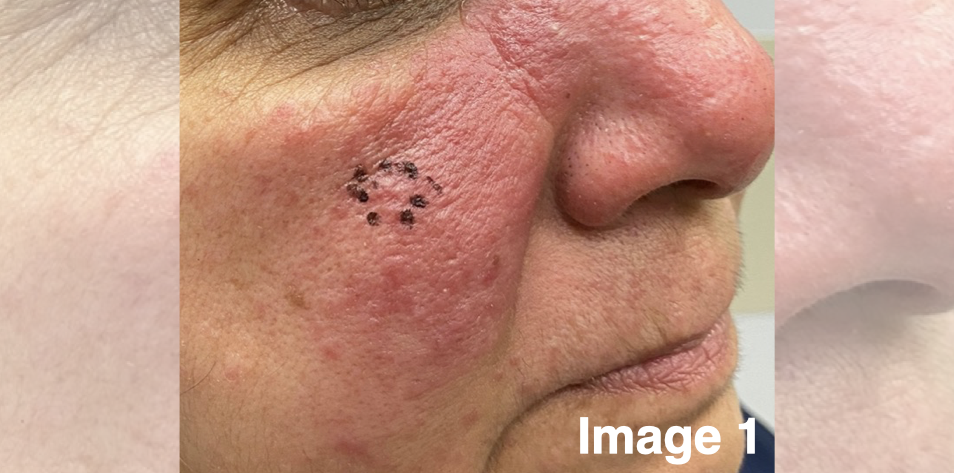
This patient was diagnosed with granulomatous rosacea, a less common rosacea variant (image 1). Granulomatous rosacea is defined as papules, nodules, and indurated plaques that affect the central face (forehead, cheeks, nasolabial folds, and perioral regions). This variant is very treatment-resistant to typical topical and oral anti-rosacea agents.
Treatment:
Follow-up visit 1 — Discussed oral isotretinoin as the main treatment option for granulomatous rosacea; risks/benefits/alternatives were discussed with the patient, and the patient agreed to start isotretinoin.
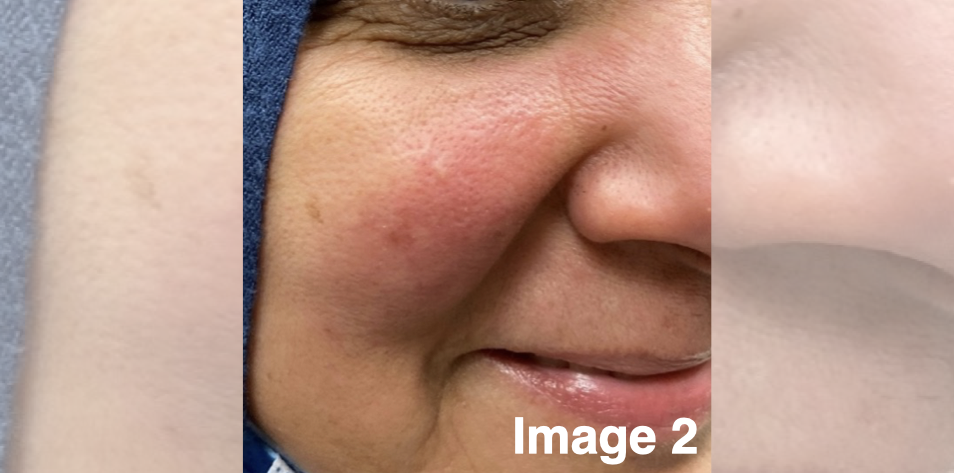
Follow-up visit 4 (5 months later) — The patient was treated with four months of isotretinoin with significant improvement in the erythema and plaque (image 2).
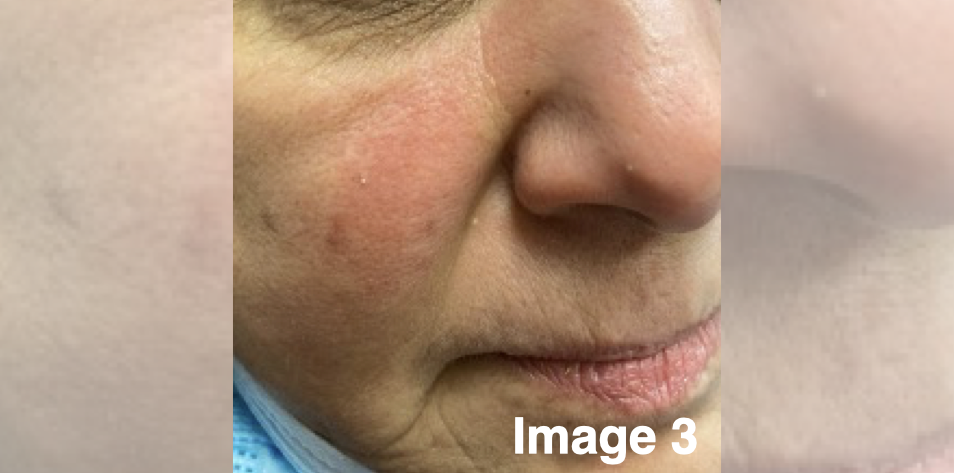
Follow-up visit 6 (2 months later) — The patient was treated with six months of isotretinoin with resolution of the granulomatous rosacea (image 3).
Clinical Pearls:
General advice for all rosacea patients is to avoid triggers that aggravate vessel dilation (hot beverages, spicy foods, chocolate, alcohol, sunlight) and wear sunscreen daily as well as sun-protective clothing, such as wide brim hats.
Topical therapies approved for rosacea: metronidazole in various formulations, ivermectin cream, sodium sulfacetamide with 5% sulfur, minocycline 1.5% foam, and 15% azelaic acid gel.
Other topicals: clindamycin lotion or solution, tacrolimus ointment, permethrin 5% cream.
Systemic therapies: tetracyclines are the mainstay therapy in rosacea (doxycycline or minocycline); alternative oral anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial options are metronidazole and azithromycin.
Isotretinoin is effective in severe papulopustular rosacea, granulomatous rosacea, and rosacea fulminans. Isotretinoin is a teratogen, and patients who can become pregnant must confirm a negative monthly pregnancy test before receiving refills. Isotretinoin dosage varies and depends on treatment response. Typically, isotretinoin starts at 0.5 mg/kg/day and is increased to 1-1.5 mg/kg/day. Treatment duration can last between 5-8 months. The most common side-effect is dry skin and lips; medication monitoring includes pregnancy (when relevant), serum liver tests, and triglyceride levels.
References
Kang CN, Shah M, Tan J. Rosacea: An Update in Diagnosis, Classification and Management. Skin Therapy Lett. 2021;26(4):1-8.
Liu Y, Zhou Y, Chu C, Jiang X. The role of macrophages in rosacea: implications for targeted therapies. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1211953. Published 2023 Aug 24. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1211953
Thiboutot D, Anderson R, Cook-Bolden F, et al. Standard management options for rosacea: The 2019 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(6):1501-1510. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.077
Published June 12, 2024
Want more clinical cases?
Join Figure 1 for free and start securely collaborating with other verified healthcare professionals on more than 100,000 real-world medical cases just like this one.